Share and Follow
For some, the simple act of eating can transform into a daily struggle marked by frustration. This challenge, known in medical circles as dysphagia, manifests as difficulty in swallowing food, liquids, or medication. To shed light on the underlying causes and offer potential remedies, we delve into expert perspectives that provide valuable insights for those seeking relief.
Why Can’t I Swallow? The Two Main Culprits
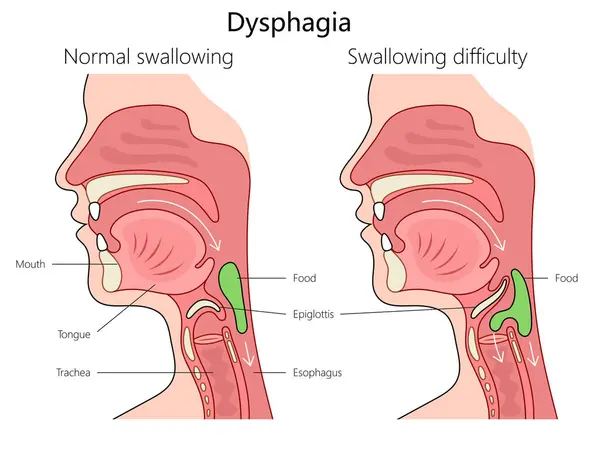
Dysphagia often arises from two primary sources: disruptions in the throat’s neurological or muscular functions, and physical obstructions or narrowings within the esophagus. The first scenario involves the miscommunication or miscoordination of nerves and muscles, which is prevalent in conditions such as stroke or Parkinson’s disease. These issues, classified as oropharyngeal dysphagia, affect the initial phase of swallowing, often resulting in coughing or an immediate sensation of food being stuck.
On the other hand, esophageal complications also play a significant role. Factors like strictures due to acid reflux scarring or tumors pressing against the esophagus create bottlenecks, particularly affecting the passage of solids and leading to discomfort. Dr. Anish Sheth, Chief of Gastroenterology at Penn Medicine Princeton Health, explains that these mechanical failures can disrupt the coordination of over 50 muscles involved in the swallowing process. With up to 16 million adults in the U.S. experiencing chronic dysphagia, many remain undiagnosed until serious complications, such as aspiration pneumonia, emerge. That uncomfortable gagging feeling at mealtime might be rooted in these underlying issues, turning eating into an ongoing challenge.
Does Swallowing Become More Difficult as We Get Older?
As people age, natural changes in swallowing mechanics become more apparent. After the age of 60, muscle tone in the throat and esophagus diminishes, a condition referred to as presbyphagia. This age-related dysphagia results from slower nerve impulses and a decrease in saliva production, complicating the formation of a bolus, or food mass, and extending transit times through the pharynx. Such delays increase the risk of choking during meals.
Take Sarah, a 72-year-old retiree, who began noticing that solid foods were becoming lodged partway down her throat. Her physician attributed this to reduced relaxation of the cricopharyngeus muscle, a typical change associated with aging. These alterations can lead to malnutrition, as evidenced by studies indicating that up to 30% of nursing home residents report swallowing difficulties linked to frailty. Preventive measures, such as softer diets, offer some relief, but additional factors, like dry mouth caused by medication, can exacerbate these issues. As we age, the seamless coordination of swallowing becomes more demanding, necessitating early attention to prevent minor annoyances from developing into significant health concerns.
Can’t Swallow Pills?
Pill dysphagia plagues about 40% of adults, who manage food and drink fine yet battle capsules and tablets. Large sizes trigger a gag reflex, while coatings stick to dry throats, mimicking esophageal spasms. Fear of choking compounds this, creating a mental block where anxiety tenses throat muscles further.
A patient once described tiny vitamins feeling like golf balls; this stems from poor head positioning or insufficient liquid chasers. Surveys reveal 1 in 3 skip doses due to this, risking health setbacks. The pro tip? Use the lean-forward technique: place the pill on your tongue, sip water without tilting back, then lean forward to let gravity and natural swallow propel it down smoothly. Practice with candy builds confidence. This method succeeds for 89% in trials, bypassing the need to crush meds that demand whole ingestion. Next time a prescription looms, tilt forward—relief awaits without embarrassment.
When to See Your Doctor for Difficulty Swallowing
Seek medical help if swallowing woes persist beyond a few days or accompany weight loss, chest pain, or regurgitation. These red flags signal serious issues like esophageal cancer or achalasia, where the lower sphincter fails to relax. Sudden onset post-stroke warrants immediate evaluation to prevent aspiration.
Hoarseness, drooling, or frequent pneumonia also demand urgent care, as they indicate neurological decline or Zenker’s diverticulum—a pouch trapping food. Doctors use endoscopy or barium swallows to pinpoint causes. Delaying risks dehydration; one report notes 50% of untreated cases lead to emergency visits. Heed these cues—early intervention restores normalcy.
What to Do If You Have Trouble Swallowing
Start with upright posture and small bites, tucking your chin to protect airways during swallows. Thicken liquids if needed, using approved gels to slow flow for safer passage. Speech therapists teach maneuvers like the supraglottic swallow, holding breath to close the airway.
For esophageal relief, proton pump inhibitors ease GERD inflammation. Hydrate well before pills, avoiding dry mouth culprits like antihistamines. Anecdotes abound: one man overcame spasms via dilation procedures, resuming steak dinners. Track symptoms in a journal for your doctor. These steps bridge to professional therapies, enhancing quality of life.
The Bottom Line on Trouble Swallowing
Dysphagia disrupts more than meals—it signals treatable conditions demanding prompt action. From aging muscles to hidden strictures, understanding triggers empowers management. Adopt the lean-forward pill trick and monitor changes closely. Consult experts like Dr. Sheth’s peers for tailored fixes. With vigilance, swallowing regains ease, ensuring nutrition and joy return to every bite.
