Share and Follow

Weather forecasters sometimes warn of storms that unleash such unusual rain they are described as 100-year or even 500-year floods.
Here’s what to know about how scientists determine how extreme a flood is and how common these extreme events are becoming.
What does a 100-year flood mean?
Scientists use math to help people understand how unusual a severe flood is and how to compare the intensity of one flood to another.
According to the U.S. Geological Survey, one statistic scientists use is the percentage chance that a flood of a specific magnitude will happen. A 500-year flood means such an event has a 1 in 500 chance, or 0.2%, of occurring in a year.
Another concept scientists use is how frequently an event of a certain intensity is expected. For example, a meteorologist can look at the average recurrence interval of an anticipated flood and see that a similar event is only expected once every 25 years.
Agencies have preferred expressing the percent chance of a flood occurring rather than the recurrence interval because that statistic better represents the fact that rare floods can happen within a few years of each other. It’s sort of like rolling a pair of dice and getting double six’s twice in a row. It’s rare, but statistically possible.
Another term people hear during an impending flood is that it could be a once-in-a-generation or once-in-a-lifetime event, a casual way of saying a flood could be unlike anything many people have experienced.
How flooding is changing with the climate
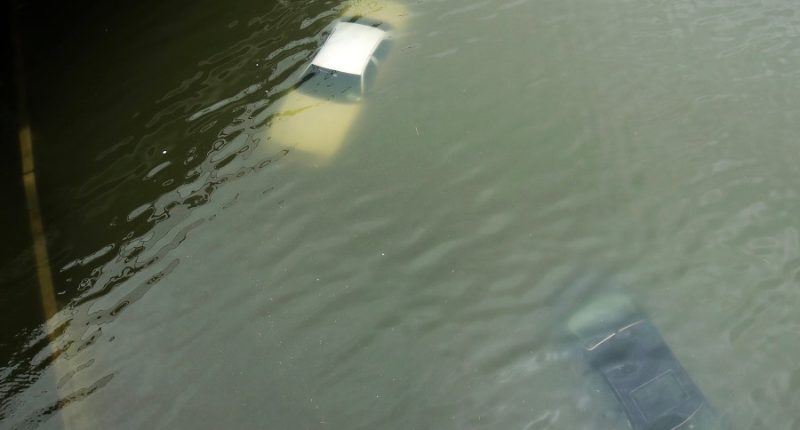
Researchers from the University of Chicago calculated that Houston, Texas, was struck by three 500-year flood events within 24 months from 2015 through 2017. The events included Hurricane Harvey, the heaviest recorded rainfall ever in the U.S. Homes and businesses were destroyed and cars were swept away by the floods.
Although math can calculate how often to expect floods of specific magnitudes, nature has its own plans, including irregularity. Many interconnected systems in the environment, such as local weather patterns and larger events like El Nino, can contribute to the changing likelihood of floods.
Since the early 1900s, precipitation events have become heavier and more frequent across most of the U.S. and flooding is becoming a bigger issue, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Gases emitted by humans, like carbon dioxide and methane, are warming the atmosphere, allowing it to hold more water vapor. For every 1 degree of Fahrenheit that the temperature warms, the atmosphere can hold nearly 4% more water, which is a 7% increase for every 1 degree Celsius, said Victor Gensini, professor of atmospheric sciences at Northern Illinois University. That vapor eventually falls back to the ground as rain or snow. “We’ve absolutely seen a shift in the probability distribution of heavy rainfall over the last three decades,” Gensini said.
Other regions have experienced drought due to changing precipitation patterns. According to NASA, major droughts and periods of excessive precipitation have been occurring more frequently. Globally, the intensity of extreme wet and dry events is closely linked to global warming. ___
Seth Borenstein contributed to this report from Washington, D.C.
___
The Associated Press’ climate and environmental coverage receives financial support from multiple private foundations. AP is solely responsible for all content. Find AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, a list of supporters and funded coverage areas at AP.org.