Share and Follow
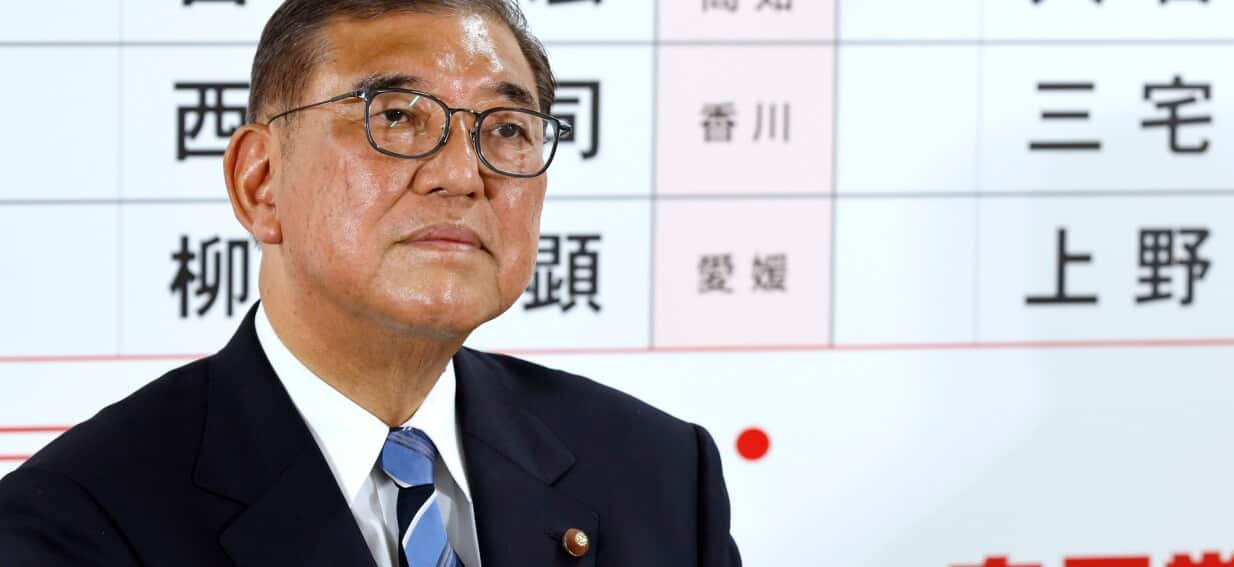

Japanese Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba has vowed to remain in office after his ruling coalition suffered a defeat in upper house elections, prompting some of his own party to deliberate on his future.
Ishiba told a news conference he would remain in office to oversee tariff talks with the United States and other pressing matters, such as rising consumer prices that are straining the world’s fourth-largest economy.
Oxford Economics’ lead Japan economist Norihiro Yamaguchi said: “The political situation has become fluid and could lead to a leadership change or the reshuffling of the coalition in coming months, but Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba will likely stay to complete the tariff negotiations with the US for now.”
‘Harsh result’
Ishiba’s Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) and coalition partner Komeito returned 47 seats, short of the 50 seats it needed to ensure a majority in the 248-seat upper chamber in an election where half the seats were up for grabs.
That comes on top of its worst showing in 15 years in October’s lower house election, a vote that has left Ishiba’s administration vulnerable to no-confidence motions and calls from within his own party for leadership change.
Speaking after exit polls closed, Ishiba told NHK he “solemnly” accepted the “harsh result”.
“We are engaged in extremely critical tariff negotiations with the United States … we must never ruin these negotiations. It is only natural to devote our complete dedication and energy to realising our national interests,” he later told TV Tokyo.
Asked whether he intended to stay on as premier, he said: “That’s right.”
‘Japanese First’ campaign
Japan, the world’s fourth-largest economy, faces a deadline of 1 August to strike a trade deal with the US or face tariffs in its largest export market.
The main opposition Constitutional Democratic Party finished second with 22 seats.
Meanwhile, the right-leaning Sanseito party announced its arrival in mainstream politics, winning 14 seats on top of its single existing seat.
Launched on YouTube a few years ago, the populist party found wider appeal with its “Japanese First” campaign and warnings about a “silent invasion” of foreigners.