Share and Follow
“We’re projecting a 20 per cent drop in bilateral foreign aid to the region by 2026,” she said.
China favours infrastructure, loans
After reducing its annual Southeast Asian development spend by 68 per cent over five years, China boosted its financing in 2023.

Source: Supplied
The regional superpower is still favouring market-rate loans for infrastructure projects, with rail ventures in Indonesia and Malaysia accounting for most of the annual increase.
China is on track to overtake traditional partners in infrastructure spending, quadrupling its commitments from 2022 to 2023 through the revival of the Kyaukphyu Deep Sea Port Project in Myanmar.
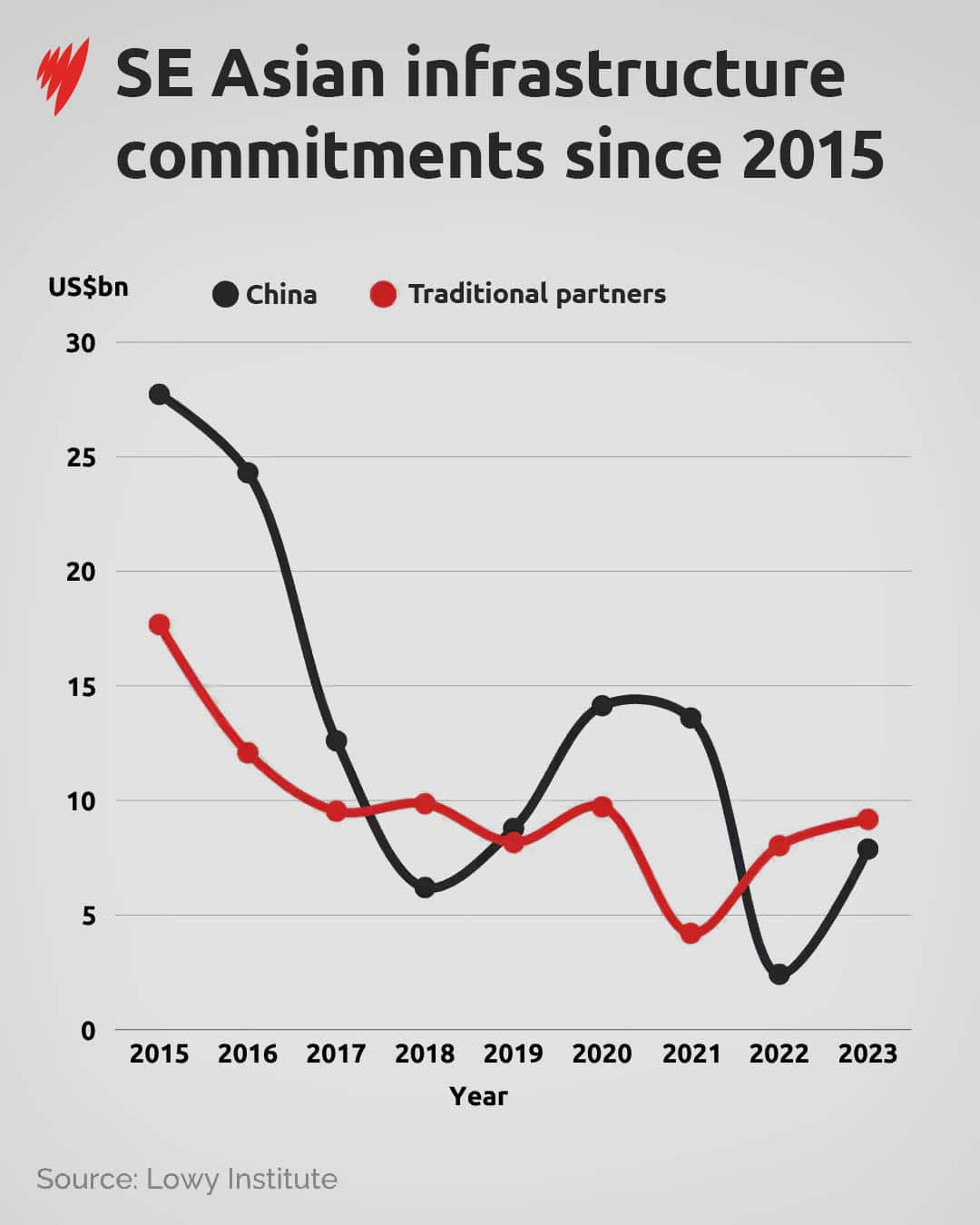
Infrastructure spending commitments by both China and traditional partners to Southeast Asian nations have decreased since 2015. Source: SBS News
It’s the loans to the region’s poorest countries — like Myanmar, Laos, and Cambodia — that have some concerned.
“I think we can expect to see less pressure for reform in terms of China’s development finance offering if there are no viable alternatives,” she said.
“That’s a huge problem if countries can’t provide the services that they need to their citizens because they’re paying back debt,” she said.
Further cuts expected
The Lowy Institute says that will result in the “centre of gravity” shifting in Southeast Asian development financing.
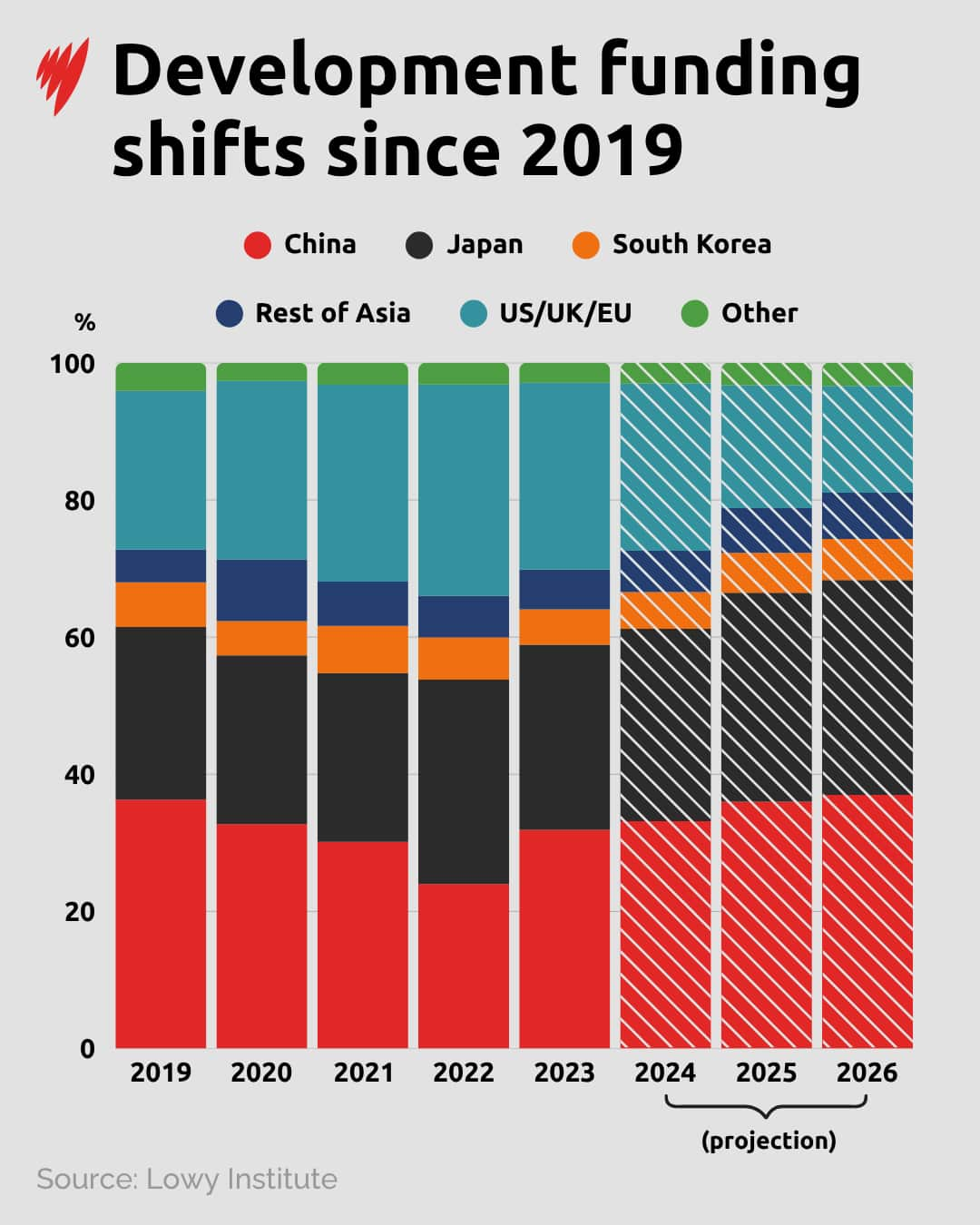
A bar chart shows the shifts in development funding from various nations since 2019. Source: SBS News
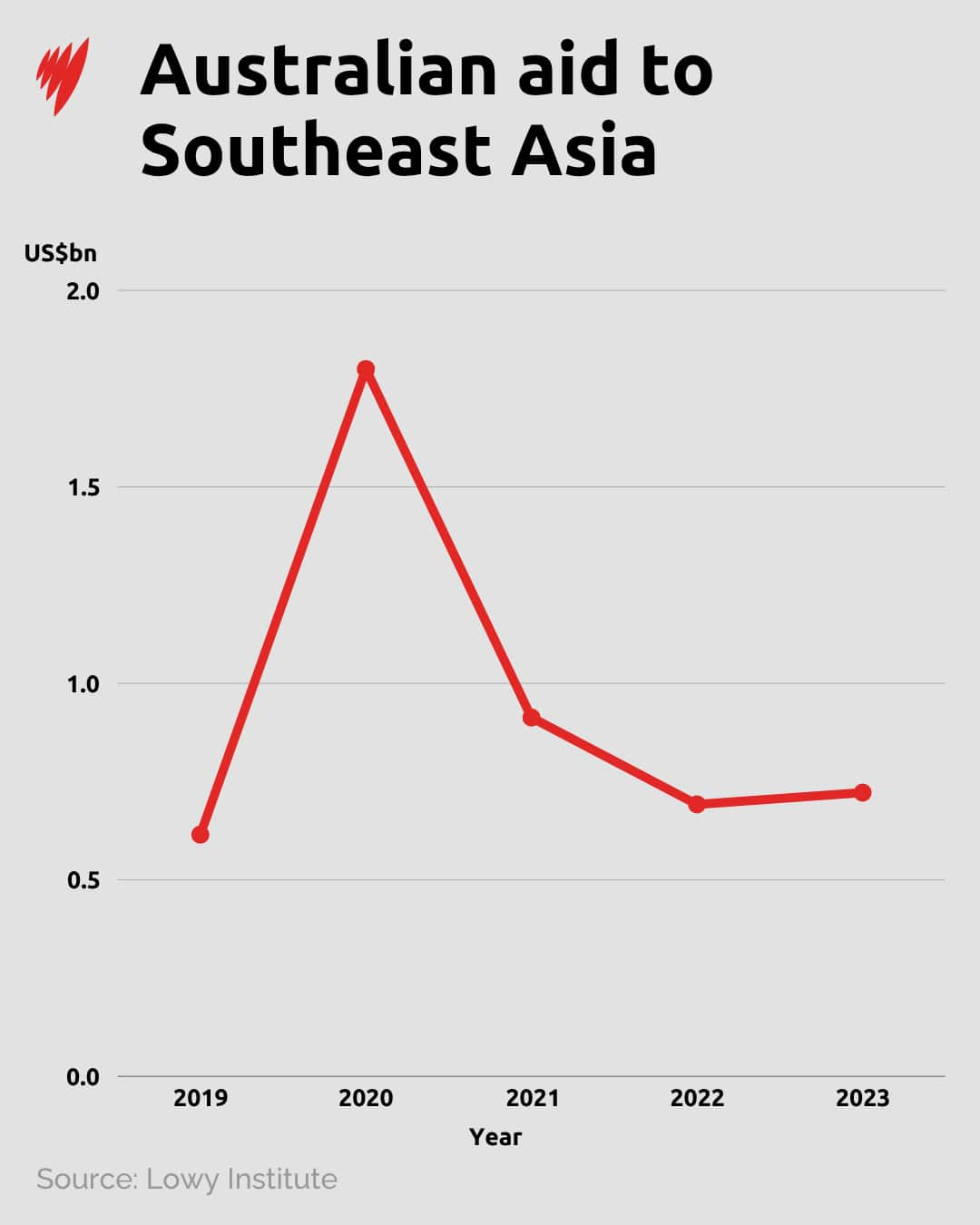
Australia’s response
“Some 75 cents in every dollar that Australia provides in development assistance is directed to our broader region,” Wong said. “We will continue to prioritise that.”
Source: SBS News
Conley-Tyler said it’s critical for Australia to maintain that focus.










