Share and Follow
It provides a resting place for seals and walruses and acts as an ‘engine’ for ocean currents.
And its vast whiteness also reflects sunlight back to space to help keep our planet cool – a weapon in the fight against global warming.
However, Antarctic sea ice, which surrounds the south pole, has shrunk to a near-record low.
On February 25th, the Antarctic sea ice hit its lowest point for the year, spanning 722,000 square miles (1.87 million square kilometers), as per recent EU data.
This marks the seventh lowest minimum extent on record, tied with 2024 – and eight per cent below the 1993–2010 long-term average.
Experts say it’s decreasing overall on a long-term basis due to global warming, largely due to humans burning fossil fuels.
‘There is far less sea ice coverage than the historical average,’ said Claire Yung, an Earth sciences researcher at Australian National University.
‘Throughout Antarctica, sea ice cover is very low this year – a reminder of the serious and unprecedented changes to Earth’s climate happening all around us.’

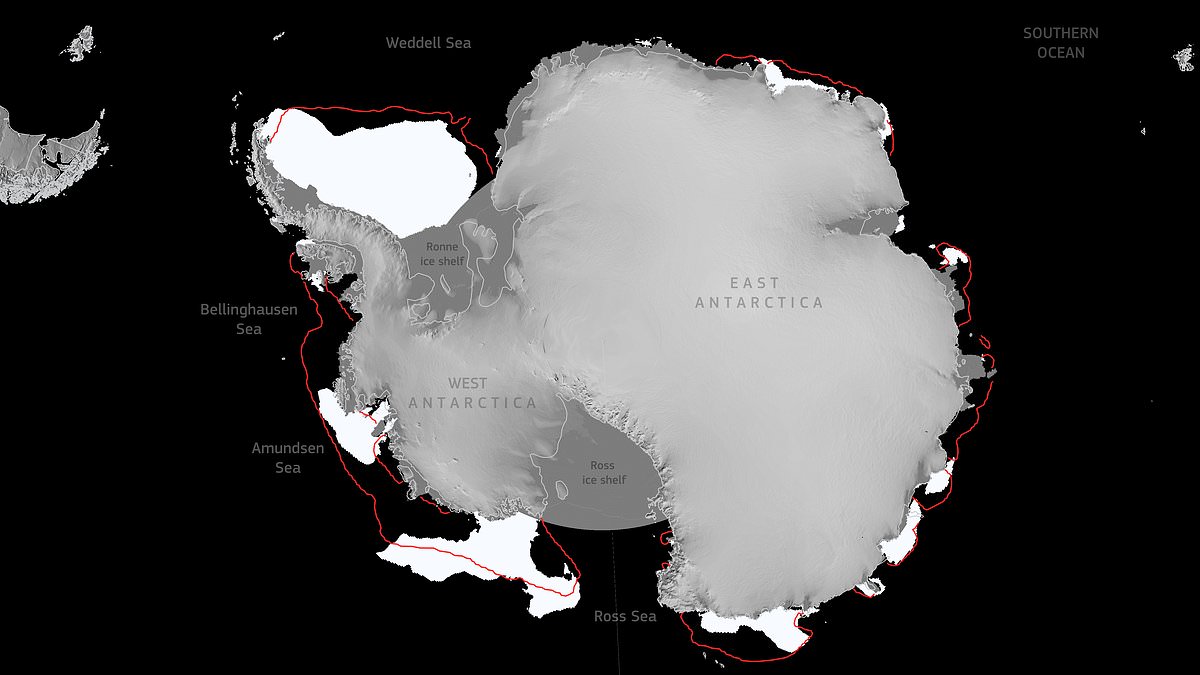
Sea ice in the Antarctic has dropped to a near-record low, according to the EU’s Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S). This map shows sea ice extent for February 25 as well as the average ice extent for February (marked by the red line)

On 25 February, the Antarctic sea ice reached its minimum extent for the year, covering 72,200 sq miles (1.87 million sq km), according to Copernicus data
The new maps and data published by the EU’s Copernicus Marine Service, are based on radiation data and visible imagery from satellites, which are constantly measuring sea ice extent.
As the maps show, there’s been a great ice loss all around Antarctica, but there are some regional variations, described as ‘uneven melting’.
For example, sea ice in the Weddell Sea and along the coasts of the Bellingshausen Sea, Wilkes Land, and Amery Land is resisting massive melting.
Antarctica’s ‘sea ice extent’ refers to total region covered by ice around the coastline of Antarctica, and does not include the ice covering the landmass itself.
The sea ice reaches a largest extent in the southern hemisphere’s winter (July to September) due to more frigid temperatures.
But temperatures gradually rise and the sea ice melts, eventually reaching a minimum extent during the southern hemisphere’s summer (December to February).
Climate scientists are constantly tracking sea ice extent throughout the seasons and comparing its size with the same months from previous years, in order to see how it’s changing.
So although there’s great variability in the ice extent depending on time of year, it’s lower than the average since records began, regardless of the season.

The surface of the ocean around Antarctica freezes over in the winter and melts back each summer. Antarctic sea ice (pictured) usually reaches its annual maximum extent in mid- to late September (winter), and reaches its annual minimum in late February or early March (summer)

Sea ice in the Weddell Sea and along the coasts of the Bellingshausen Sea, Wilkes Land and Amery Land is resisting massive melting
Since 2017, Antarctic sea ice minimums have consistently set record lows, highlighting a ‘concerning trend in climate change’, Copernicus said.
According to the EU agency, sea ice volume – another metric for measuring ice – has also reached near-record lows during the southern hemisphere’s summer.
On March 5, 2025, Antarctic sea ice volume reached its minimum, dropping to just 247 cubic miles (1,030 km3), it also revealed.
Worryingly, this marks a 56 per cent decrease from the long-term average of 573 cubic miles (2,390 km3).
Sea ice volume is a really important metric because it looks at how thick the ice is, as well as the distance it covers.
Often sea ice can have a great extent but its exposure to warmer temperatures has thinned it out.
Antarctic and Arctic sea ice is vitally important because the whiteness of the ice reflects the sun’s light, helping to keep polar regions cool, known as a higher ‘albedo’.
Without this ice cover, dark patches of ocean are exposed instead, which absorbs sunlight rather than reflecting it – in turn, heating up the region and accelerating ice loss further.

This graph shows daily Antarctic sea ice volume – not extent – from 1993 to 2025. Antarctic sea ice volume and extent generally reaches its maximum in the southern hemisphere’s winter (July to September) before falling

Sea ice provides a resting and birthing place for seals and walrus, a hunting and breeding ground for polar bears, and a foraging ground for arctic fox, whales, caribou, and other mammals. Pictured: a polar bear on ice in the Arctic Sea

Also this week, NSIDC has revealed that Arctic sea ice (which is at its greatest extent around this time of year) is at a record low. Arctic sea ice reached 5.53 million sq miles (14.33 million sq km) on March 22 – likely its maximum extent for the year
‘We’re losing Earth’s albedo, and many don’t realize the severe consequences,’ said Peter Dynes, managing director of non-profit organization MEER.
Arctic sea ice also provides a resting and birthing place for seals and walrus, a hunting and breeding ground for polar bears, and a foraging ground for arctic fox, whales, caribou, and other mammals.
A lack of ice and poor ice conditions cause stress for marine mammals and ultimately affect their livelihoods and abilities to reproduce, according to the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC).
Rapid warming has already caused a significant southward shift and contraction in the distribution of Antarctic krill – a keystone species, campaigners said.
Also this week, NSIDC has revealed that Arctic sea ice – which is at its greatest extent around this time of year – is at a record low.
Arctic sea ice reached 5.53 million sq miles (14.33 million sq km) on March 22 – likely its maximum extent for the year.
Although this might sound high, it’s the lowest in the 47-year satellite record, falling short of the previous record low of 5.56 million sq miles (14.41 million sq km ) set on March 7, 2017.